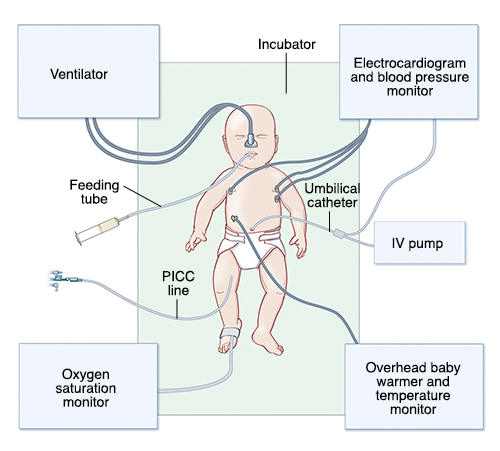
Equipment in the NICU
These devices are often used while a baby is in the NICU (neonatal intensive care unit):
-
Incubator. This is the clear plexiglass box that makes up your baby’s bed. This enclosed space protects the baby from temperature changes. A radiant warmer over the bed may be used instead of an incubator to keep the baby warm. A cloth cover can be placed over an incubator to keep out noise and light.
-
Cardiorespiratory monitor. This keeps track of the baby’s heartbeat and breathing. It’s attached to the baby’s skin with 3 leads (sensors). These are held in place with a gel that’s gentle to the skin.
-
Pulse oximeter. This measures the level of oxygen (called oxygen saturation) in the baby’s blood. It’s attached to the skin with a sensor taped to the baby’s hand or foot. It works by shining a light through the baby’s hand or foot.
-
Blood pressure monitor. This may be a smaller version of the blood pressure cuff used on older children and adults. Or an arterial catheter (tiny tube inserted in an artery) may be used to keep track of blood pressure.
-
Temperature probe. This measures the baby’s body temperature. It’s attached to the skin surface.
-
IV (intravenous) line. This is a small, flexible tube (catheter) inserted into a vein. It’s used to give the baby fluids, nutrition, and medicines.
-
Umbilical arterial catheter or umbilical venous catheter. This tube is placed in the artery or vein at the stump of the umbilical cord. It’s used to give the baby medicines, fluids, and nutrition. It’s also used to draw blood for lab tests. Because there are no pain nerves in the umbilical cord, putting the line in and maintaining it causes the baby no pain. But there is a higher risk of complications with an umbilical catheter than with an IV.
Other devices you may see
-
Feeding tube (gavage tube). This goes through the mouth or nose into the stomach. It's used to feed the baby milk or formula.
-
CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure) machine. This delivers air or oxygen through tubes in the nostrils. It uses low, continuous pressure to keep the lungs inflated.
-
Endotracheal tube (ETT). This goes through the baby's mouth or nose into the windpipe. It's used with a respirator or ventilator to send air directly to the lungs.
-
Respirator or ventilator. These machines may be used to help the baby breathe. They are attached to an ETT.
-
Peripherally inserted central catheter or a percutaneous central venous catheter. This tube may be inserted in a central (large) vein. It's used to give the baby fluids, nutrition, and medicine.
Online Medical Reviewer:
Donna Freeborn PhD CNM FNP
Online Medical Reviewer:
Heather M Trevino BSN RNC
Online Medical Reviewer:
Liora C Adler MD
Date Last Reviewed:
10/1/2022
© 2000-2024 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.